 org.biomoby.service.BaseService
org.biomoby.service.BaseService
|
Version: 1.1.1 | |||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||
java.lang.Objectorg.biomoby.service.BaseService
public abstract class BaseService
A base class for all Biomoby services (if their providers choose to
write their services this way, of course). It contains basic
features expected from any SOAP-based Web service (such as an
access to the initialization parameters - see methods getParamNames() and getParam(java.lang.String)), and also features expected
from any Biomoby Web service (such as parsing input XML data and
creating smoothly XML output data).
This base class does not contain any service-specific entities. It serves all Biomoby services. The service-specific features (notably the method that is called when a service is invoked) are in the generated service skeletons (a separate skeleton for every service). A service provider extends a service skeleton by her/his own class that implements service business logic but does not need to deal with the Biomoby protocol/envelope at all.
Here is the basic inheritance picture of involved classes for a Biomoby service registerd (in a Biomoby registry) under the name "A_Service":
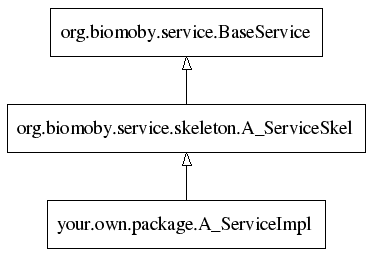
A typical generated skeleton (for service "A_Service") would look like this:
abstract public class A_ServiceSkel
extends BaseService {
public String A_Service (Object data) {
try {
// reading the whole input
MobyPackage mobyInput = MobyPackage.createFromXML (data);
// prepare an output object
MobyPackage mobyOutput = prepareOutput (mobyInput);
// do the main job
processIt (mobyInput, mobyOutput);
// and return an XML back
return mobyOutput.toXML();
} catch (MobyException e) {
return error (e.getMessage());
}
}
}
|
While a service provider class (implemented manually) could look like this (its name is arbitrary):
public class AServiceImpl
extends A_ServiceSkel {
public void processIt (MobyJob request,
MobyJob response,
MobyPackage outputContext)
throws MobyException {
// this is how to get input data
GenericSequence input = get_GenericSequence (request);
String seq = input.get_SequenceString();
// this is an example of a trivial "business logic"
response.setData (new MobyInteger (seq.length()));
}
}
|
Note that this particular service uses an input object of type GenericSequence and an output object of type Integer - but if a more specific object, such as a NucleotideSequence comes from a client, it will handle it properly.
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
BaseService()
Default constructor. |
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
String |
error(String message,
MobyPackage outputSoFar)
Error handling. |
String |
getCallerAddr()
Returns the Internet Protocol (IP) address of the client or last proxy that sent the request. |
Properties |
getHTTPHeaders()
Returns HTTP headers that were used when delivering a request to this services. |
String |
getParam(String name)
Get value of a parameter 'name'. |
String[] |
getParamNames()
Return a list containing the parameter names available within the context of the invoked web service together with the global context. |
int |
getRequestLength()
Returns length (in bytes) of the request coming to this service. |
javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest |
getServletRequest()
Returns a servlet request instance - the one that delivered a request to this service. |
org.tulsoft.tools.soap.SOAPToolkit |
getToolkit()
Return a toolkit that gives you broader access to the environment where this service is deployed in. |
static boolean |
isEmpty(String value)
A utility method returning true if 'value' is either null or a string consisting only from whitespaces. |
static boolean |
notEmpty(String value)
A utility method returning true if 'value' is neither null nor a string consisting only from whitespaces. |
MobyPackage |
prepareOutput(MobyPackage mobyInput)
Return a package that has the same number of jobs (and named the same) as the given input. |
abstract void |
processIt(MobyJob request,
MobyJob response,
MobyPackage outputContext)
A job-level processing: This is the main method to be overriden by a service provider! |
void |
processIt(MobyPackage mobyInput,
MobyPackage mobyOutput)
A high-level processing. |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
equals, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait |
| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public BaseService()
| Method Detail |
|---|
public String[] getParamNames()
Any web service (deployed within a reasonable environment, such as Apache Axis) can be deployed with some initialization parameters that are static (they do not change during the Web Service) and they are, of course, not changeable not even visible to the service clients. Typical example would be parameters needed for a JDBC connection (JDBC URL, user name, password etc.).
getParam(java.lang.String)public String getParam(String name)
getParamNames().
name - of a parameter
public org.tulsoft.tools.soap.SOAPToolkit getToolkit()
See details what a toolkit can provide in org.tulsoft.tools.soap.SOAPToolkit.
public javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest getServletRequest()
public String getCallerAddr()
public Properties getHTTPHeaders()
public int getRequestLength()
The length is taken from the HTTP headers. This is only a
convenient method extracting one header from those available by
the getHTTPHeaders. >p>
public static boolean notEmpty(String value)
public static boolean isEmpty(String value)
public String error(String message,
MobyPackage outputSoFar)
This method produces an empty (no data) response with the 'message' in its service notes tag. Whatever is returned by this method is send back to the client. So if you override it, you must return back an XML (if you wish the Biomoby client to understand/parse it).
message - is a reason why this method was called in the
first place; it is a good practise to incorporate it (somehow)
in the return valueoutputSoFar - is a so-far-filled response (it may be
null); you may consider to use it and to fill its service notes
tag with the 'message', or you can ignore it and create your
own error response
public MobyPackage prepareOutput(MobyPackage mobyInput)
throws MobyException
Usually, there is no need to override this method. It is called by a service skeleton, once an input XML is parsed and before a service implementation class is called to process it.
mobyInput - contains all data coming from a client
MobyException - if input data package is corrupted
public void processIt(MobyPackage mobyInput,
MobyPackage mobyOutput)
throws MobyException
processessig on the job
level.
mobyInput - contain all data coming from a clientmobyOutput - is an empty package that will go later to the
client; this method should fill it with a response
MobyException - if processing failed; in which case the
caller of this method (which is usually a generated skeleton)
will probably call the error(java.lang.String, org.biomoby.shared.parser.MobyPackage) method
public abstract void processIt(MobyJob request,
MobyJob response,
MobyPackage outputContext)
throws MobyException
This method is called once for each job in a client
request. A job is a
BioMoby query (in a client request), or a result of one query
(in a service response). There can be more queries (jobs) in
one network request to a BioMoby service. If a network request
contains more jobs, also the corresponding service response
must contain the same number of jobs.
request - contain data coming from one client's jobresponse - is an empty object (except its name that is
already filled in - because it must correspond with the same
name in the 'request'); this method should fill it with a
responseoutputContext - is a package that will be, at the end,
delivered to the client; it is here not to be filled - that is
taken care of by some other methods - but you may use it to see
how other (previous) jobs have been made, and also to add
things to the package envelope (e.g. service notes)
MobyException - if a complete processing failed; after
this exception the client will not get any data back (only an
error message). If you wish just to indicate that only this
particular job failed you have to add an exception to the
outputContext - see MobyPackage.addException(ServiceException,MobyJob).
|
Version: 1.1.1 | |||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||