The parser itself is in the class {@link org.biomoby.shared.parser.MobyParser MobyParser} that is accompanied by a list of all Biomoby's XML tags and attribute names stored in the {@link org.biomoby.shared.parser.MobyTags MobyTags} class.
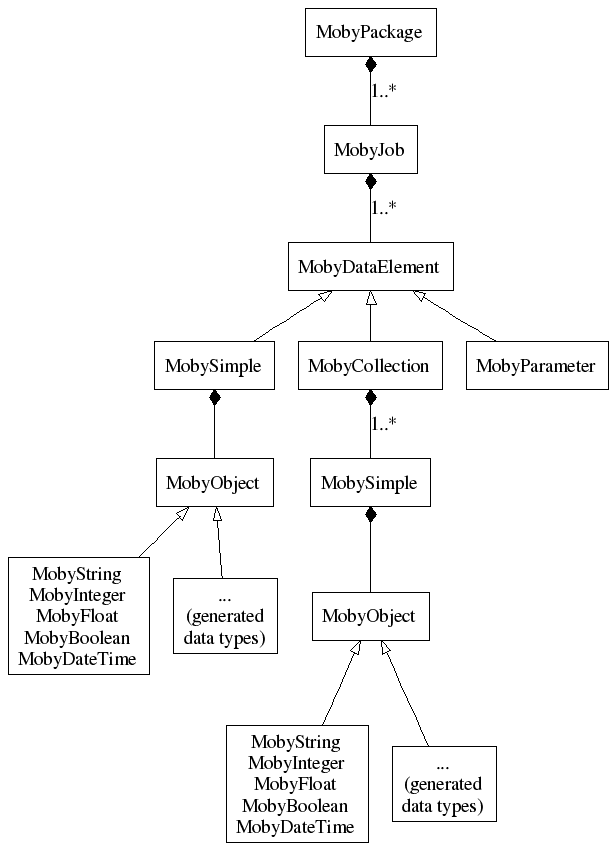
Java objects representing parsed data start with {@link org.biomoby.shared.parser.MobyPackage MobyPackage} - the main container (that also invokes parser itself). A MobyPackage instance corresponds to one network call to a Biomoby service, or to a response from such service.
Here is a full example how to get parsed Biomoby XML data into a MobyPackage (note that the input XML - the variable data in the example - can be given as a String, byte[], or a File which conveniently corresponds with the requirement from the Biomoby API):
try {
MobyPackage mobyInput = MobyPackage.createFromXML (data);
// here do something with 'mobyInput'
} catch (MobyException e) {
System.out.println (e.getMessage());
}
To bring data back into XML is again simple:
try {
// fill response data into a mobyOutput...
MobyPackage mobyOutput = new MobyPackage();
...
// and convert it into XML
String xml = mobyOutput.toXML();
} catch (MobyException e) {
System.out.println (e.getMessage());
}
A MobyPackage then contains one or more {@link
org.biomoby.shared.parser.MobyJob MobyJob}s each of them containing
one "execution" (or a "query" in a Biomoby speak). Note that a
Biomoby service must be able to accept more invocations (jobs,
queries) from one network request. A MobyJob can also carry a
response from a service. Again, data coming from a service can consist
from more responses - actually the number of the MobyJob
objects in a response must be exactly the same as a number of the
MobyJob objects in the originated request. A MobyJob has the data themselves - they are either stored in {@link org.biomoby.shared.parser.MobySimple MobySimple}s or in {@link org.biomoby.shared.parser.MobyCollection MobyCollection}s. The number and types of these {@link org.biomoby.shared.parser.MobyDataElement MobyDataElement}s are defined for each Biomoby service in a Biomoby registry.
The MobySimples have data stored in various data objects - their classes are in the package {@link org.biomoby.shared.datatypes}. The primitive data types are there available directly, the other types can be generated (see details in the package itself).
Here is a picture showing how the entities are relates:
